
There’s no stress like water stress.
I know, I’ve been living it for 20 years.
A proportion (25% to 100%) of the water used in hydraulic fracturing is not recovered, and consequently this water is lost permanently to re-use, which differs from some other water uses in which water can be recovered and processed for re-use.
Alberta DROUGHT 12:12 Min by Kyle’s Forecasts Jan 24, 2024
Sundre begins planning for possible 2024 drought, Alberta Environment and Protected Areas minister advising municipalities that action may be required to fully prepare for possible severe drought this year by Simon Ducatel, Jan 18, 2024, Mountain View Today
SUNDRE – The municipal council has directed administration to develop proactive drought protection and prevention measures including a water shortage plan in preparation for a possible drought this year.
The Town of Sundre administration has also been tasked with looking into the possibility of introducing some kind of rebate or subsidy program for residents interested in conservation upgrades such as rain barrels as well as timers for lawn and garden watering systems.
As Alberta braces for the soberingly distinct possibility of extreme drought conditions this summer, the minister of Environment and Protected Areas has asked municipalities to begin drafting up water shortage plans in the event of a worst-case scenario that leads to provincially-imposed restrictions.
Council discussed the issue in-depth on Jan. 8 during the first regular meeting of the new year. Coun. Paul Isaac, who informed administration in advance that he could not attend, was the only absence.
Providing some background information, Linda Nelson, chief administrative officer, said correspondence had been received from Rebecca Schulz, minister of Environment and Protected Areas, who “is advising municipalities and municipal leaders that action may be required to fully prepare for severe drought in 2024.”
Alberta has a five-stage ranking system for drought severity in its water management plan, with Stage 5 presenting a province-wide emergency.
“Currently, we are at Stage 4,” said Nelson.
The CAO went on to outline some of the proactive steps the municipality has already taken over time in an effort to reduce water waste, including an underground utility assessment study that identified priority projects in the capital plan as well as leak-detection equipment purchased years ago that has proved effective at locating leaks.
“The Highway 27 underground project, which replaces pipes that we believe are up to 50 years old, has identified at least two major leaks which will be repaired with the completion of this project,” she said, adding the recently approved 10-year capital plan includes numerous other major upgrades to underground infrastructure that is expected to substantially reduce water lost to leakage.
Additionally, a water conservation bylaw was adopted in 2019. However, Nelson suggested initiating a review process to update the bylaw since the document is already five years old.
Further, she said the municipality will have to draft a water shortage plan in coordination with provincial officials, and also recommended distributing public information sheets outlining water conservation tips, such as a brochure mailed out in utility bills.
The environment minister’s two-page letter, which does not mention climate change or the many heat records that were shattered around the world in 2023 – now officially by far the hottest year since records began – states that “several water basins reached critical drought conditions due to low rainfall and high temperatures.”
The situation has been exacerbated by the first global El Niño phenomenon in seven years, Schulz wrote.
“It’s causing less snow and rain, along with higher temperatures, heightening the potential for significant drought into spring and summer 2024, particularly in southern Alberta,” she said.
The minister also outlined what the provincial government is doing, including but not limited to establishing a drought command team as well as working to refine an early draft of the 2024 Drought Emergency Plan, striking an advisory panel, and to initiate drought modelling efforts that will help “determine how to maximize the province’s water supply.”
She added action at the municipal level will also be required, and outlined four steps to take:
• initiate efforts to monitor water supply infrastructure proactively, paying particular attention to water intake relative to water levels;
• begin a review of the terms of your municipality’s water licence so you are aware of any conditions that may limit your ability to withdraw water during a drought;
• alert municipal water managers to prepare to be engaged with officials from the Drought Command Team, should conditions within your municipal water licence need to be triggered; and
• develop a water shortage plan so your municipality is prepared to respond if water availability decreases.
The minister also said the government is “asking all water users to start planning now to use less water in 2024.”
Coun. Chris Vardas started the roundtable discussion and said conversations about water conservation will be ongoing over the coming years as times continue to change. Speaking against the idea of scheduling specific days and times when people are allowed to water lawns, Vardas suggested instead looking into the possibility of helping offset the cost for those who are interested in installing timers.
“If everybody put a timer on their watering system in their yards, it only waters it from this time to this time for an hour, an hour and a half. That’s where we would conserve,” he said. “If you look at the data, anybody that’s on that kind of system, they conserve a lot more than the average bear.”
Coun. Jaime Marr said the government’s website outlines numerous tips to save water that could also be further promoted by the municipality along with a general advisory about the situation.
“I thought maybe in our utility bill, we could just sort of pre-emptively let people know that we’re looking at this; that this could be coming to the forefront. We’re already at level 4,” said Marr, adding she also supports the idea of timers.
“Although I think if we’re in a water shortage and hit a (Stage) 5, there’s going to be no watering lawns anyway. But I do worry about gardens, because a lot of people have raised garden beds,” she said, mentioning water-catching methods like rain barrels are also among the government’s tips.
However, while Coun. Todd Dalke said he agreed with province-wide conservation efforts, he pointed out Sundre sits on the Red Deer River.
“I’ll be that guy. Aren’t we glad we live in Sundre ’cause the water comes out of the ground by itself?” said Dalke, expressing a reluctance to impose any additional burdens on residents, not just by way of restricting water use but also asking them to consider buying timers or barrels.
Nelson cautioned council that in the event the province announces a Stage 5 drought, the government would enact the Emergency Water Management plan, which could affect the municipality’s water licence, potentially even restricting it by up to 60 per cent.
“We may not have a choice. So, it’s good for us to get started right now,” she said.
Coun. Owen Petersen recommended a municipally-led educational campaign and also agreed with the idea of timers and barrels.
“I would even be willing to entertain the idea of the municipality subsidizing, somehow, people’s rain barrels or timers or (other) things to actually conserve water,” said Petersen.
Also speaking in favour of timers, Coun. Connie Anderson warned the idea might not be popular.
“I think you’re going to find in Sundre, people are going to say, ‘We sit on water.’ And they’re not going to like these ideas at all,” said Anderson.
Vardas recognized the municipality’s geographically fortunate location that – for now at least – provides an abundance of water.
“But if there’s no ice caps on the mountains, there’s no water trickling down,” said Vardas.
“You’re right, we are on water and we got plenty of it. But one day, we might not,” he said.
Through conversations the councillor said he’s had with friends who work in fracking, Vardas said, “They’re getting stressed a little bit too. Because even when it comes to fracking, they got to draw water from somewhere. And they’re saying there’s barely any water.”
Meanwhile, he said the municipality sells plenty of its treated water to fracking operations rather than drawing grey water from the lagoon.
“I don’t know why we don’t entertain that,” he said.
Nelson agreed that using treated water for fracking isn’t ideal, but added that as per the municipality’s water licence, Sundre is required to release a high percentage of treated effluent back into the river.
“If we could use water from the lagoon and subtract that off the amount that we’re putting back into the river, I agree that would be amazing. But that would take a provincial approval,” she said.
Mayor Richard Warnock said municipalities south of Calgary have been attempting to address water shortages for the past couple of years, and argued Sundre should be prepared to inform its residents what they can and cannot do if the province imposes restrictions.
Beyond the existing bylaw, the municipality should also have a colour-coded, four-stage strategy, said Warnock, who also sits on Alberta Municipalities’ Sustainability and Environment Committee, which is working on a water conservation policy for the whole province.
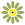
“They are concerned in the north as well,” he said, adding last year’s record fire season has emphasized the critical importance of maintaining adequate water reserves to battle wildfires.
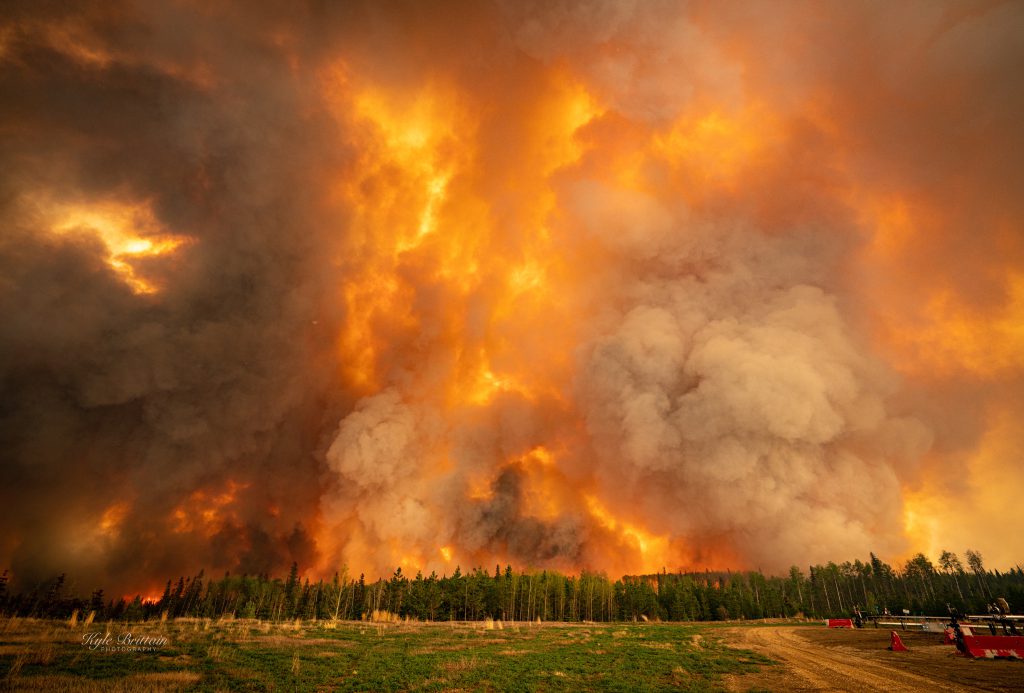

2023: Fox Creek (Alberta’s Frac Central) Wall of Fire, photo by Kyle Brittain
Ultimately, Dalke moved to direct administration to start drafting plans for proactive drought measures with further updates to come.
Speaking in favour, Petersen said one of the municipality’s strategic pillars is to be good environmental stewards and added that focusing on water conservation efforts helps not only Sundre, but also the many other Albertans who live downstream of the Red Deer.![]() That includes me, and I am already double impacted: first by Encana/Ovintiv’s illegal frac’ing of the aquifers in my community, contaminating them, next by Plains Midstream’s sour crude oil spill.
That includes me, and I am already double impacted: first by Encana/Ovintiv’s illegal frac’ing of the aquifers in my community, contaminating them, next by Plains Midstream’s sour crude oil spill.![]()

“I don’t think it’s prudent for us to just sit here and think how great it is to water our lawns and forget that there’s a huge amount of this province that relies on this water. If we do our small part, I think that’s really important,” he said.
Dalke’s motion carried unanimously.
Sundre sets 2024 fees and rates bylaw, Town of Sundre aims to place greater emphasis on user-pay cost-recovery approach for municipal services by Simon Ducatel, Nov 29, 2023, Mountain View Today
SUNDRE – A number of changes to the municipality’s fees and rates bylaw, including the addition of some new charges intended to place a greater emphasis on a user-pay cost-recovery approach, were recently approved.
Chris Albert, director of corporate services, told council during the regular Nov. 20 meeting that administrative staff monitor throughout the year how each department is faring when compared with budgeted amounts as well as how the municipality’s fees stack up with comparable communities’ services or facilities.
As per council’s direction following discussions during the recent fall workshop, Albert said the 2024 fees and rates bylaw was revised with the introduction of some new lines to place a greater emphasis on a user-pay cost-recovery approach.
The first group of fees Albert highlighted to council all pertain to planning and development and more specifically relate to the municipality’s process to apply for land use bylaw amendments, land use re-designations, as well as the subdivision application fee.
Previously, there were no fees associated with either a land use bylaw amendment request or a land use re-designation application for a single lot, he said, later adding each of those proposed charges were set at $500.
“Those are both new fees that would be established to kind of encourage development as well as ensure that we’re covering our costs,” he said.
“Our existing bylaw doesn’t break out some of the minuscule details. So, there’s kind of a larger fee that could be applicable to some smaller projects.”
The subdivision application fee, which involves matters such as land titles and engineering, is a combined rate that for 2023 was set at $1,200 and $200 – amounts proposed to be increased to $1,500 and $250 for 2024. Administration found the municipality’s costs for those services were increasing, and so felt increasing the corresponding fees was also warranted under the basis of cost recovery, he said.
The guideline administration works with relates back to the municipality’s financial framework, which essentially follows the user-pay philosophy where the cost of a utility, service or facility is to be substantially offset by the consumer, with the expense’s remaining balance being covered through general taxation, he said.
That financial framework alludes to whenever possible aiming for an approximately 60-40 split in terms of services that the municipality provides across the board, he said, adding the 60 per cent of a cost to provide a service is paid by users, with the remaining 40 per cent covered by taxes.
“What I heard at the fall workshop, was that council wants us to work harder in getting closer to that 60-40 split,” he said.
Providing additional context, Betty Ann Fountain, senior development officer, said that per the 2023 bylaw’s fee schedule, any application for a land use bylaw amendment – whether for example a request to rezone a district or simply change a single lot – would cost $2,000 plus any additional expenses that might be involved such as engineering.
However, “it didn’t seem fair to charge that $2,000” in instances when an applicant has a lot located for example downtown on an already-serviced property where there’s an existing structure in place and no engineering is required, said Fountain.
“So, $500 is cost recovery for that process,” she said.
Processing subdivision applications, however, represents a greater cost burden largely as a result of additional paperwork and consultations, she said, adding other municipalities were surveyed including Olds, Didsbury, Carstairs as well as Three Hills.
“We are at the low end” even with the proposed increase to the fees, she said, adding Olds charges $4,000 for a subdivision application alone, plus the additional cost of advertising fees and staff time presenting to council.
A few items in the bylaw outlining the cost of replacing equipment like roll-out carts as well as automatic gas as well as water meter readers were also changed to read “at-fault cost recovery” instead of a specific dollar amount, said Albert.
“What we found is because of the escalating costs, what we’d like to do is remove the specific dollar amount and put it in the fees bylaw that it is meant as a 100 per cent cost recovery,” he said, emphasizing that doesn’t apply to regular wear and tear.
“This is specifically at-fault damage,” he said. “Whatever it costs us to buy it, that’s what we’re going to be charging.”
Administration also proposed increasing fees for altered and unaltered animals.
“The amount of fees that we are collecting only covers 30 per cent of the costs that are associated with animal control,” he said, adding the municipality’s contractor for animal control declined to renew their contract at the end of the year.
“So, we are looking at doing a new contract; we are seeing those costs increase,” he said.
But even with the fee for both altered cats and dogs each going up to $20 from $11 before the Jan. 31 deadline, after which the rates increase to $40 from the former $33, the municipality remains below what comparable towns are charging, he said.
“We think this is the most reasonable amount that we can put on pet owners at this particular point in time,” he said.
Conjuring up the most conversation from council was administration’s proposal not only to increase both the flat fee as well as consumption rate for treated water, the wastewater flat fee, and gas consumption, but also the bulk water rate and the lagoon charge.
“Water and wastewater are tied very closely together. If it comes out of your tap, it goes down your sink,” said Albert.
“To each utility, there’s two ways that a consumer is charged: the first is a flat fee, the second is consumption,” he said, adding flat fees should generally be associated with debt repayment, capital repayment and fixed expenditures while consumption fees should be associated with variable expenses.
While administration proposed maintaining the wastewater consumption rate at $1.45 per cubic metre, the treated water consumption fee was increased to $2.70 from $2.25.
“There’s a lot more that has to go on with treating and distributing water versus the wastewater, which goes into the lagoon and sits,” said Albert, adding that operating costs have also been increasing over the past several years.
“But for the last five years, our rates on water and wastewater have actually remained the same,” he said, adding those numbers were brought in line.
Flat fees for both treated water as well as wastewater each went up to $23 from $21.50.
And while the flat fee for gas was set to remain the same at $26, the gas consumption rate was marginally increased by five cents to $1.50 from $1.45 per gigajoule, and the gas system improvement charge per gigajoule went up to $0.25 from $0.21.
“All the changes for these utility rates would cost the average household an extra $5 to $7 per month,” he said, adding that of course will vary among different users, especially commercial or industrial.
Despite the proposed increases, Albert said the municipality would still remain competitive with comparable communities.
Coun. Chris Vardas supported increasing the treated water consumption fee, asserting that a resident who insists on frequently watering their lawn throughout the summer should not have to be subsidized by their neighbours.
While some residents occasionally stock up on bulk water to for example fill up a hot tub, Albert said that service – as well as the lagoon dump charge – is generally used either by county residents or companies. Bulk water is a more costly service to provide and primarily ends up being used for industrial purposes, he said.
“I do believe that there should be – for lack of a better term – a penalty applied for using our treated water for non-consumption purposes,” he said, adding that if residents on average pay $5 per cubic metre of water, the bulk rate should be doubled at $10 to cover the treatment costs.
Coun. Todd Dalke said doubling that rate would be difficult to justify.
“Raising our water too high puts us at risk economically of not being a viable source for that water,” said Dalke.
Albert replied that Sundre’s rates would still be among the lower end of comparables.
“A company going somewhere else, they would be paying more; we would still be lower than what they would pay elsewhere,” he said.
Vardas had no issue with the proposed increase.
“When you’ve got truckers coming in and using treated water for a frack job or something like that, that to me should get charged to a certain degree,” he said.
“Because using treated water for fracking I think is ridiculous and we should find another source – leave the potable water for human consumption,” he said, adding the fee to dump outside sewage at the municipality’s lagoon, which reduces capacity, should also be increased.
“If they want to travel to another location – I hate to say that – but that’s their prerogative. At the end of the day, we’ve got to also take care of our residents,” he said.
Responding to a question from Dalke regarding roughly how many cubic metres of outside wastewater the lagoon treats annually, Albert estimated an average of about 15,000 m3 and added the facility process somewhere between 225,000 to 250,000 m3 every year.
When the time came for council to decide whether to approve the bylaw, Coun. Owen Petersen proposed an amendment to leave as-is the flat fees for water and wastewater.
“Flat fees, I understand the methodology and why they’re there. They also really frustrate me because when you want to make an active change in your consumption, you still get nailed with that flat fee,” said Petersen, adding he was not opposed to the consumption rate going up.
“I would much rather see, that if I want to water my lawn, then I get charged more. But right now, even if I don’t water my lawn all day long and take shorter showers, I still have to pay more.”
Recognizing the methodology behind the flat fee, the councillor expressed a philosophical disagreement and a preference for emphasizing user-pay.
“I would like the power to be in our ratepayers’ hands (so) if they want to cut costs, they can actively use less water. Period,” he said. “I would like to see the water consumption go up and the flat fee stay the same.”
His colleagues largely disagreed and countered that flat fees are an important part debt repayments. Mayor Richard Warnock said municipalities all have fixed costs that continuously increase in an inflationary economy, and added freezing those fees today would mean paying a price down the road.
Petersen’s proposed amendment was defeated with Dalke, Petersen and Coun. Jaime Marr in favour while Warnock, Vardas and councillors Connie Anderson and Paul Isaac were opposed. A motion passing the proposed bylaw as presented ultimately passed with Petersen and Dalke opposed.
Among the rates that will remain unchanged are fees for the Sundre Community Centre and the Sundre Arena as well as solid waste.
Refer also to:


A proportion (25% to 100%) of the water used in hydraulic fracturing is not recovered, and consequently this water is lost permanently to re-use, which differs from some other water uses in which water can be recovered and processed for re-use.
