Acute myocardial infarction associated with unconventional natural gas development: A natural experiment by Alina Denham, Mary D. Willis, Daniel P. Croft, Linxi Liu, and Elaine L. Hill, Environmental Research, Volume 195, April 2021, 110872, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.110872
Highlights
Long-term exposure to unconventional gas development increases heart attacks.
Heart attack hospitalizations increase 1.4–2.8%, depending on age and sex.
Heart attack mortality increases 5.4% in middle-aged men.
Abstract
Background
Whereas it is plausible that unconventional natural gas development (UNGD) may adversely affect cardiovascular health, little is currently known. We investigate whether UNGD is associated with acute myocardial infarction (AMI).
Methods
In this observational study leveraging the natural experiment generated by New York’s ban on hydraulic fracturing, we analyzed the relationship between age- and sex-specific county-level AMI hospitalization and mortality rates and three UNGD drilling measures. This longitudinal panel analysis compares Pennsylvania and New York counties on the Marcellus Shale observed over 2005–2014 (N = 2840 county-year-quarters).
Results
A hundred cumulative wells is associated with 0.26 more hospitalizations per 10,000 males 45-54y.o. (95% CI 0.07,0.46), 0.40 more hospitalizations per 10,000 males 65-74y.o. (95% CI 0.09,0.71), 0.47 more hospitalizations per 10,000 females 65-74y.o. (95% CI 0.18,0.77) and 1.11 more hospitalizations per 10,000 females 75y.o.+ (95% CI 0.39,1.82), translating into 1.4–2.8% increases. One additional well per square mile is associated with 2.63 more hospitalizations per 10,000 males 45-54y.o. (95% CI 0.67,4.59) and 9.7 hospitalizations per 10,000 females 75y.o.+ (95% CI 1.92,17.42), 25.8% and 24.2% increases, respectively. As for mortality rates, a hundred cumulative wells is associated with an increase of 0.09 deaths per 10,000 males 45-54y.o. (95% CI 0.02,0.16), a 5.3% increase.
Conclusions
Cumulative UNGD is associated with increased AMI hospitalization rates among middle-aged men, older men and older women as well as with increased AMI mortality among middle-aged men. Our findings lend support for increased awareness about cardiovascular risks of UNGD and scaled-up AMI prevention as well as suggest that bans on hydraulic fracturing can be protective for public health.
Refer also to:
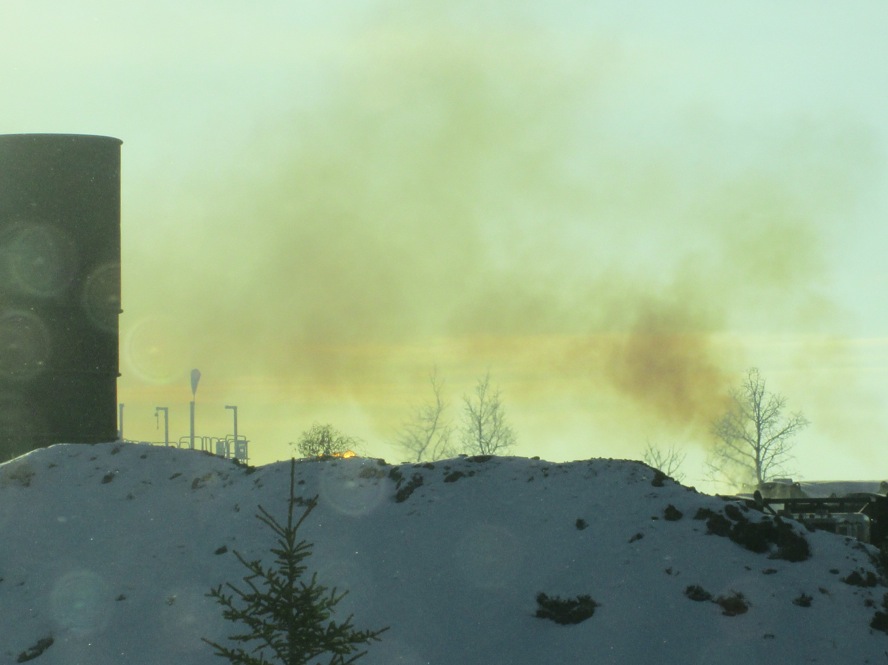



One frac site in Alberta, of thousands. Imagine what the harmed are breathing.
etc.
etc.
etc.
